PDGuide - Analyzing Performance and Debugging Problems Using Trace
Appearance
Reprint Courtesy of International Business Machines Corporation, © International Business Machines Corporation
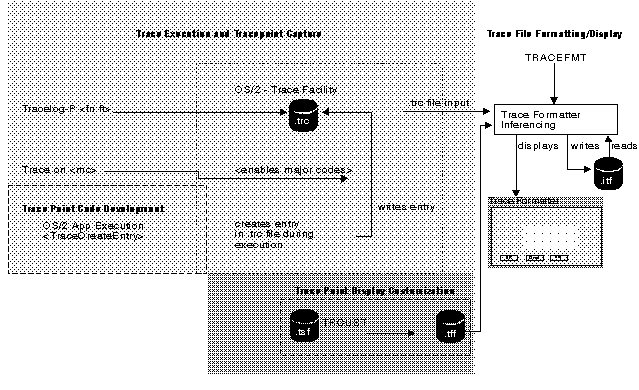
This chapter describes trace and the benefits of the various types of trace points. The chapter contains an overview of instrumenting (setting up) your code to use trace and explains how to display and analyze trace information.
This chapter also describes the following programs that are used to analyze trace information:
- Trace Formatter (TRACEFMT)
- Trace Commands (TRACE and TRACEBUF)
- Trace Customizer (TRCUST)
- Trace Capture (TRACEGET)
TraceFlow